Mapping the Iraqi Entrepreneurial Ecosystem: Growth Domains, Involved Actors, and Leading Programs
KAPITA’s Research Team
Research Summary
Overview
As Iraq has been transitioning from a socialist economy, based on a welfare state model, into a more capitalist economy. The entrepreneurship scene has been developing over the last decade in a very evident way. Many support organizations, training centers, institutions, coworking spaces, etc., have emerged and led to the proliferation of the scene, where many startups have been founded, transforming the Iraqi economy by attracting investors and creating job opportunities. This has also encouraged the development of financial technologies, policies, and infrastructure to keep up with this transformation.
Therefore, this research aims to track down the entrepreneurial growth over the years in Iraq by properly structuring the ecosystem into categories and creating a database for entrepreneurs, founders, SMEs, stakeholders, investors, and many other actors who are involved in the development of the Entrepreneurial Ecosystem. The research offers a roadmap for the main actors by presenting the collected results as a series of infographics which could serve as a reference point and a guide to advise future actions for all the actors within the ecosystem.
Research Methodology
The research followed four main steps to ensure an inclusive and satisfactory coverage of the Iraqi entrepreneurial ecosystem.
Structuring the Iraqi ecosystem into categories following a hybrid of two main resources, which are: “Guide for Mapping the Entrepreneurial Ecosystem” by GIZ and the “Entrepreneurial Ecosystem Diagnostic Toolkit” by ASPEN. Additional modifications were adopted to these approaches to accommodate the different features of the current Iraqi entrepreneurial scene.
Collecting the relevant data to the entrepreneurship scene in Iraq by a team of researchers. The data included general information about the actors involved in the entrepreneurial ecosystem, and detailed the actions of each of these actors and where does it fit within the ecosystem. The data was collected through online sources including but not limited to websites and social media.
Verifying the collected data with some of the main actors of the Iraqi entrepreneurial scene to reduce the margin of error and the biases that could be raised by unilateral efforts.
Designing a series of infographics based on the collected information to make the data easier to digest and visually more appealing.
Research Data
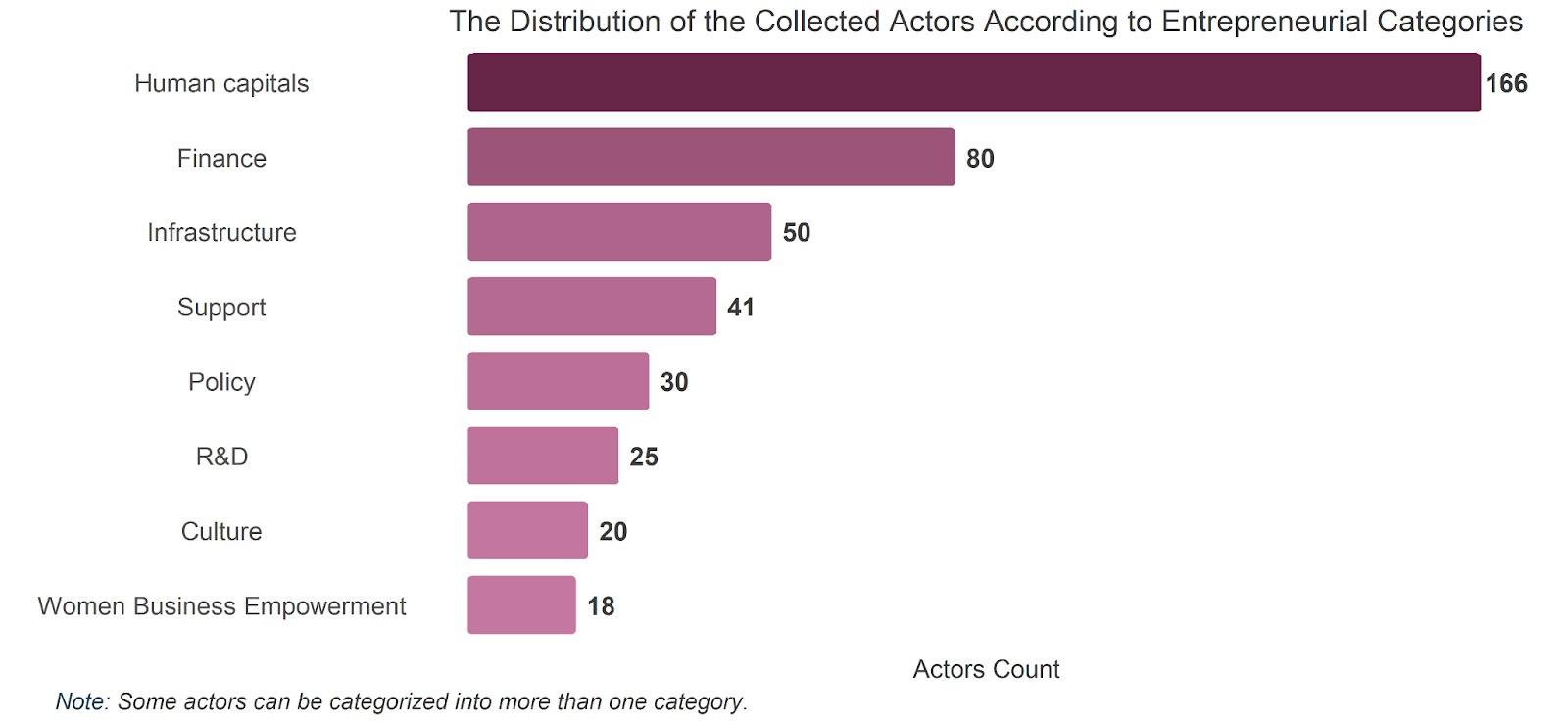
The number of relevant actors that were collected for this research totaled to 379 actors each with several entrepreneurial actions. The graphs below show the distribution of these actors across the main eight categories.
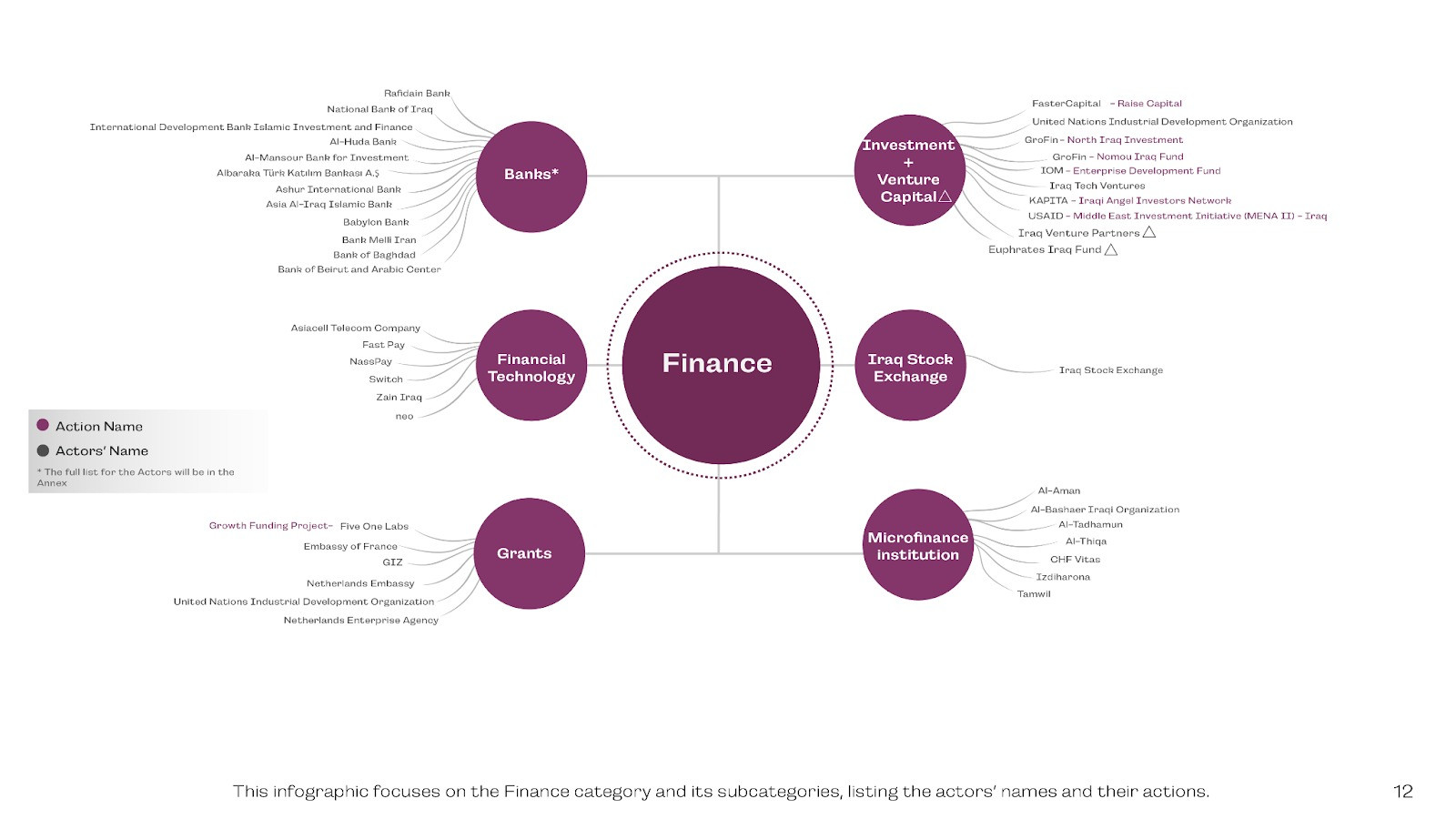
The database was created in such a way that the ecosystem is categorized into eight main categories, each with its own subcategories. These categories are Support, Finance, Human Capital, Research & Development, Policy, Culture, Women Business Empowerment, Human Capital, and Infrastructure.
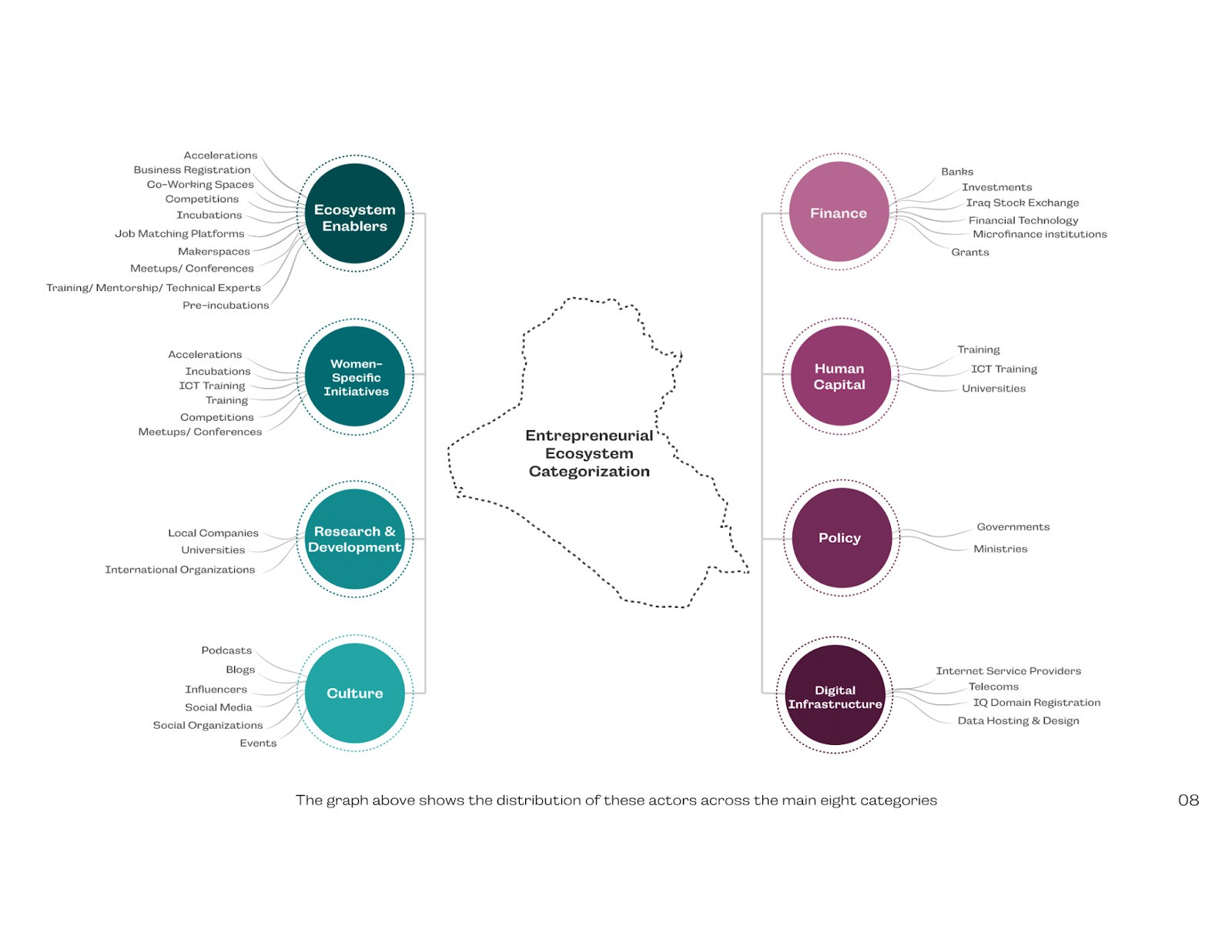
Research Findings
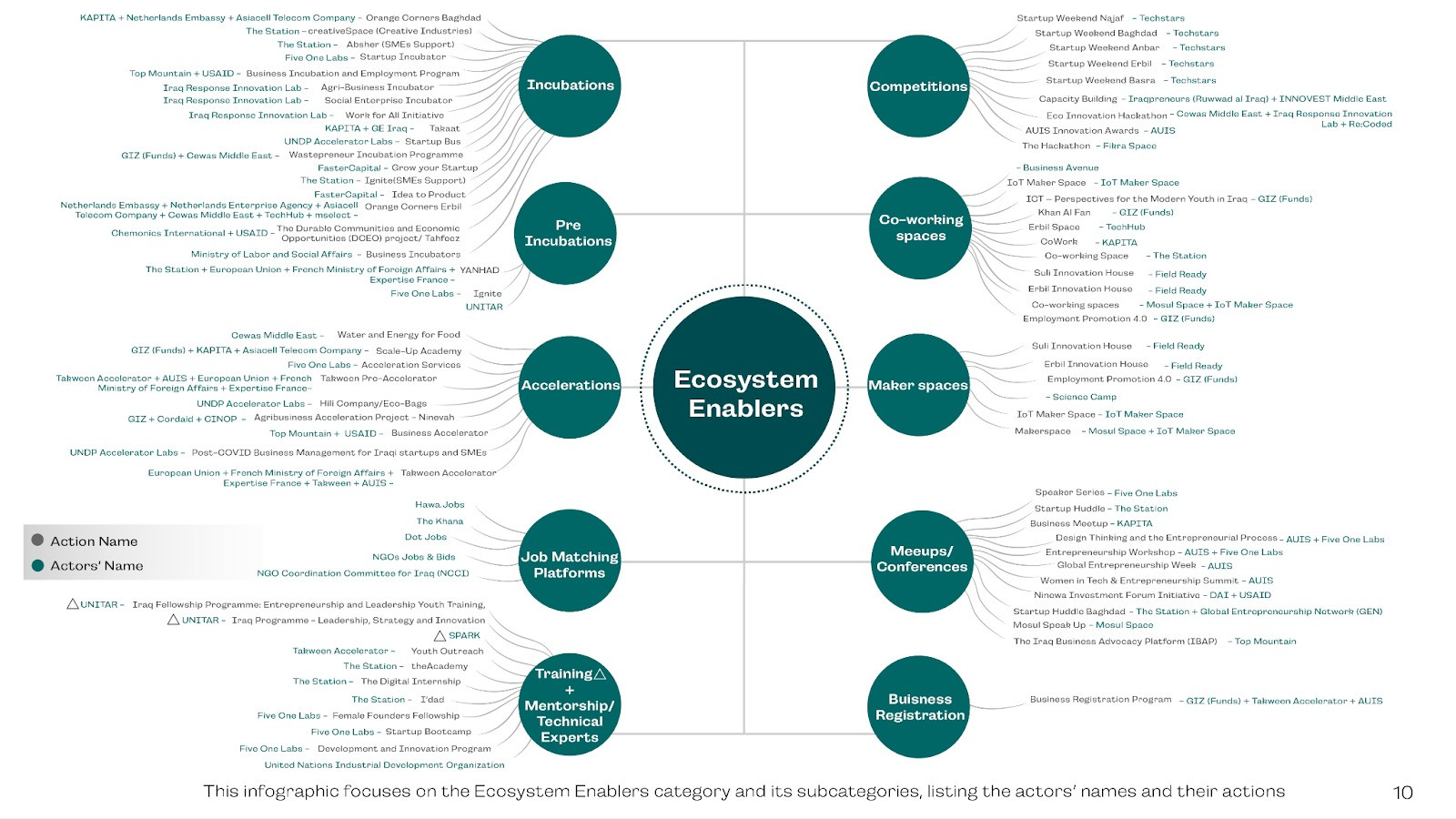
Ecosystem Enablers
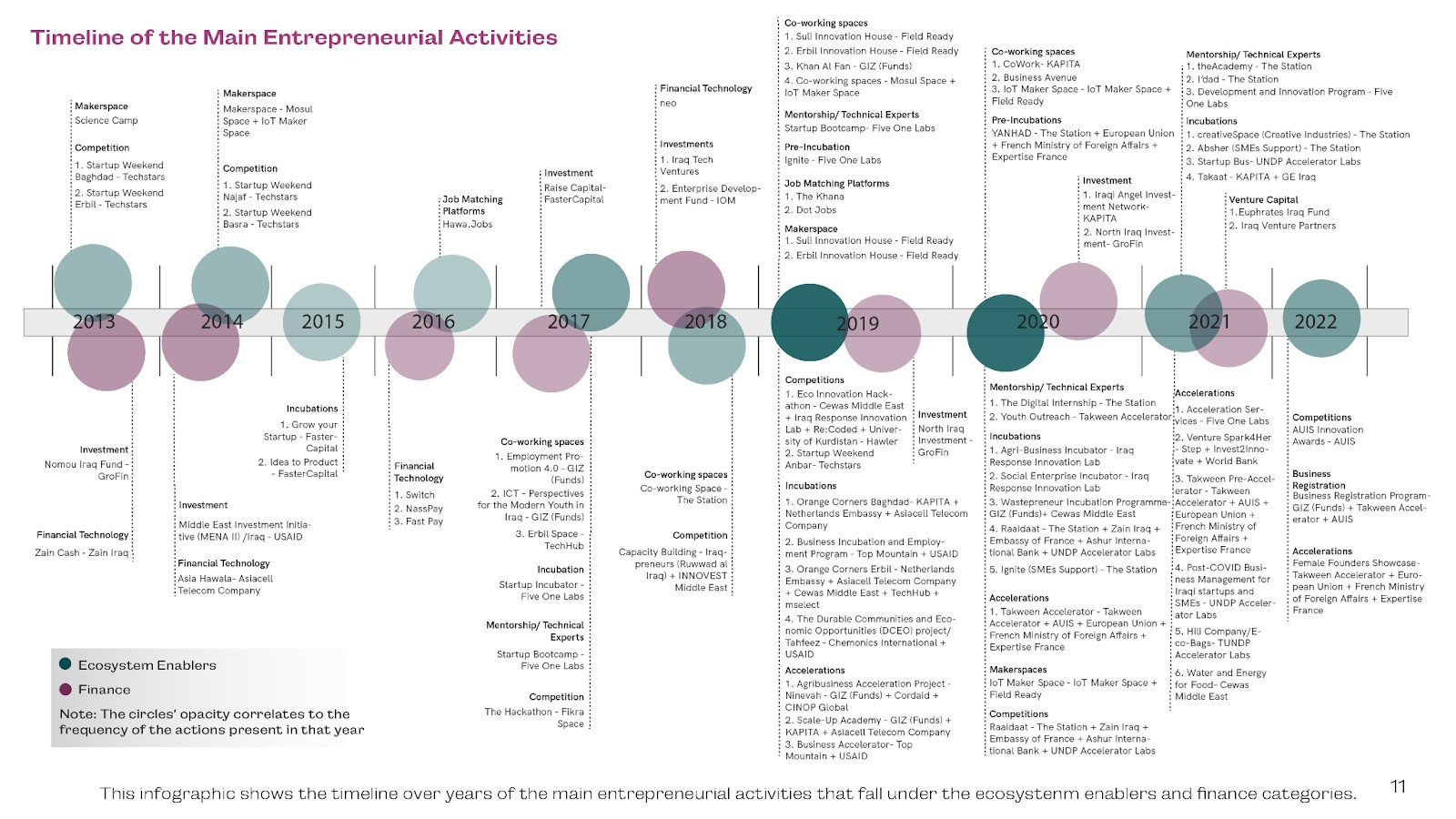
Finance
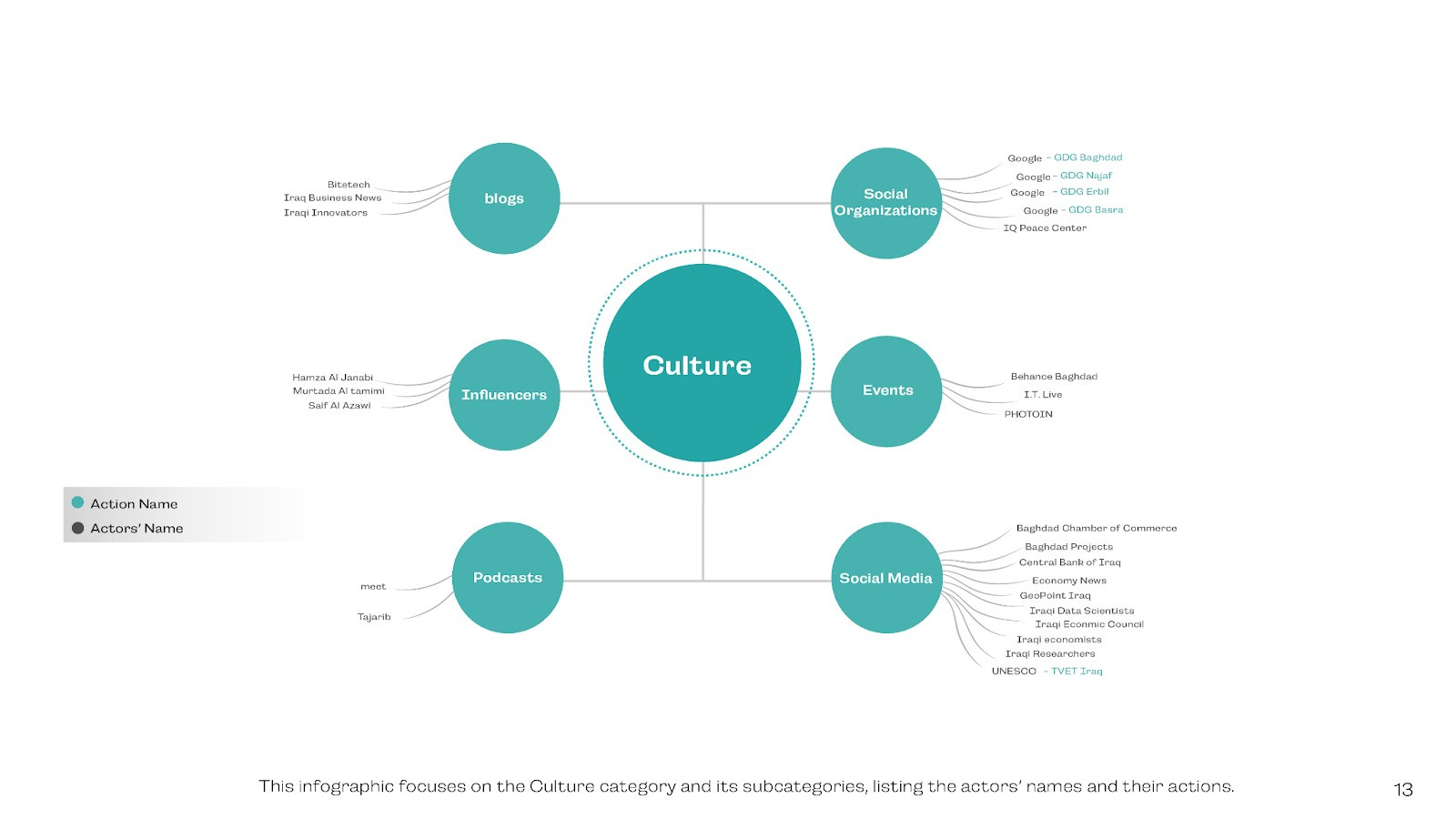
Culture
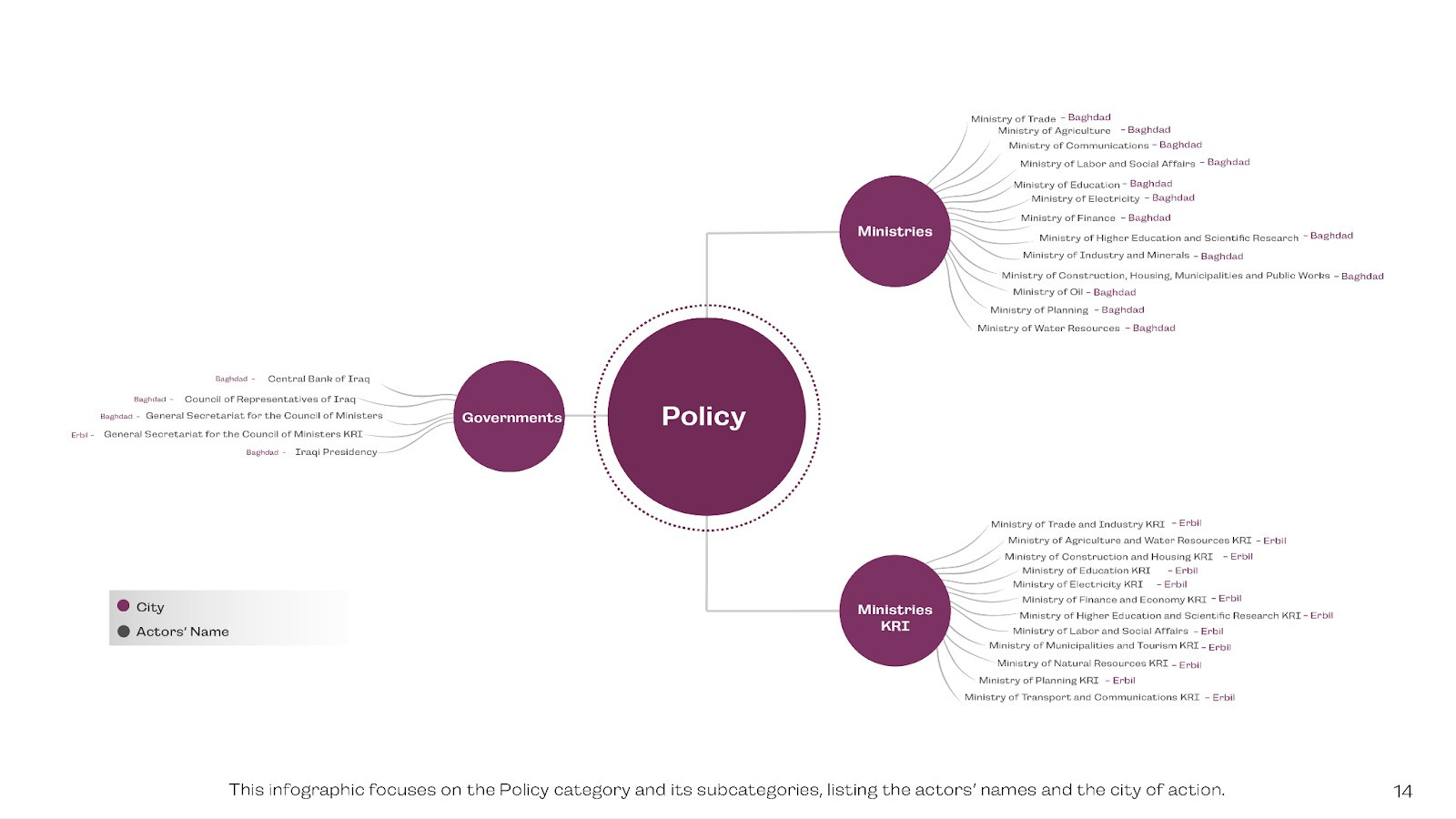
Policy
Research & Development

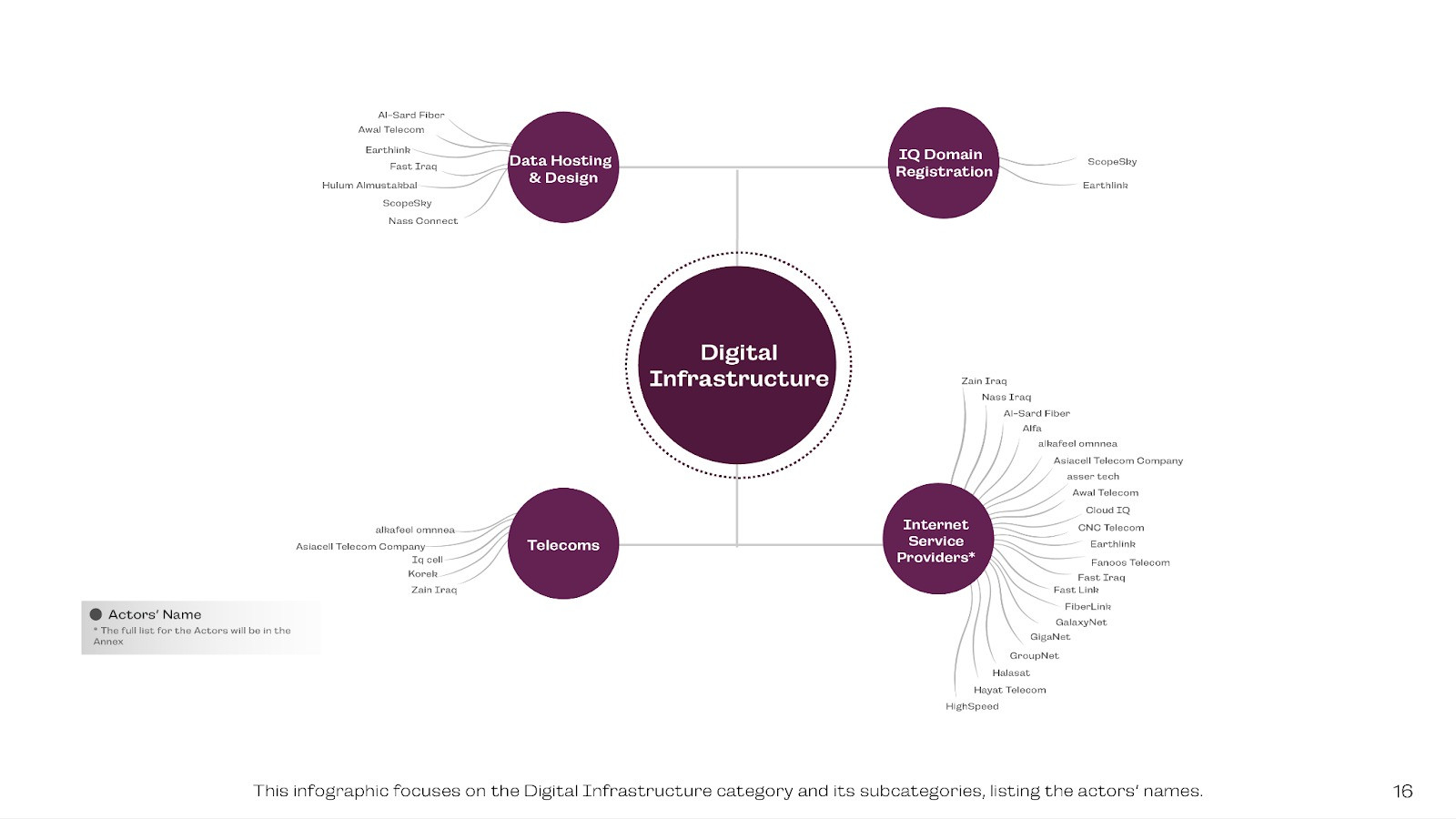
Digital Infrastructure
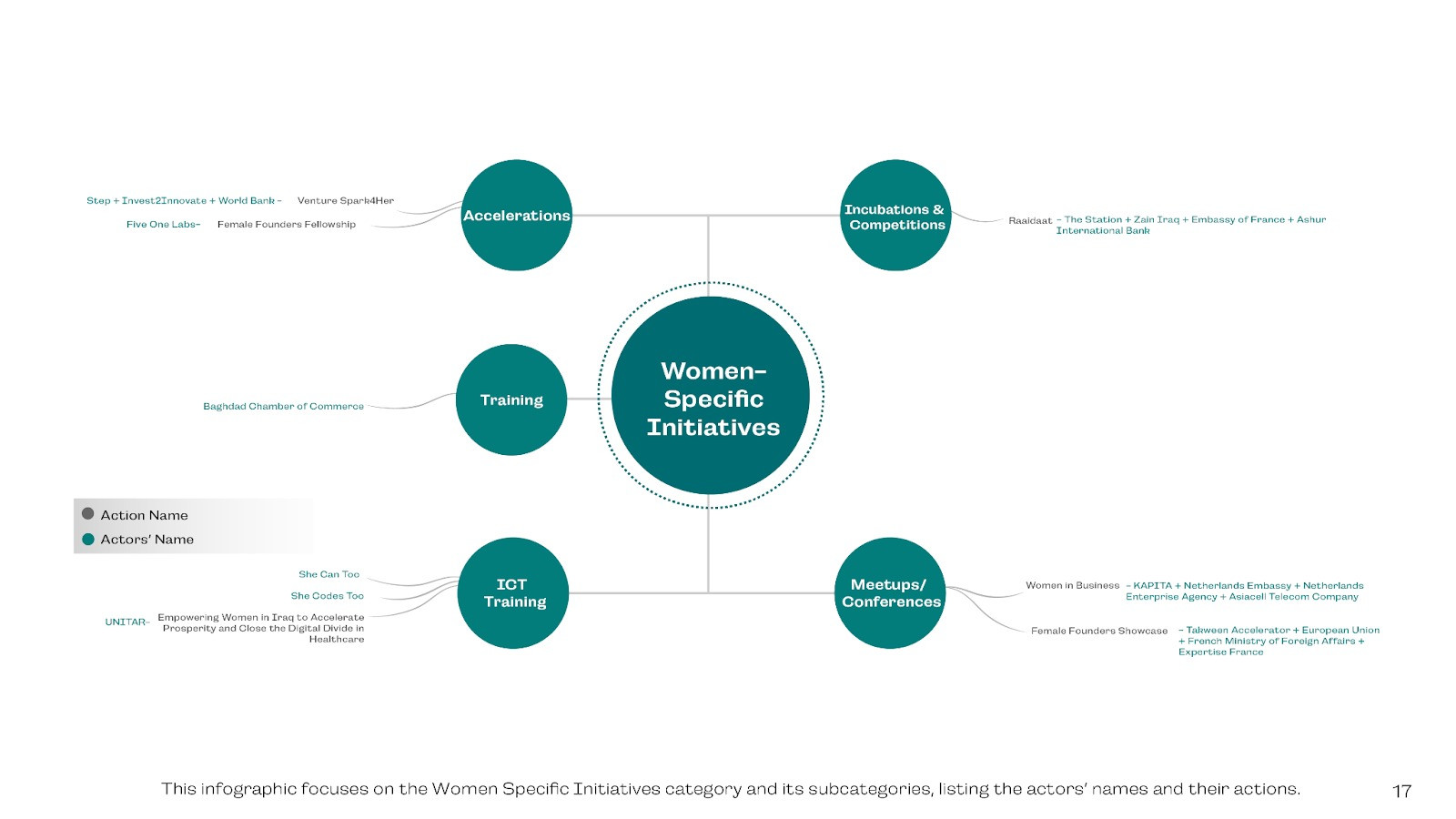
Women-Specific Initiatives
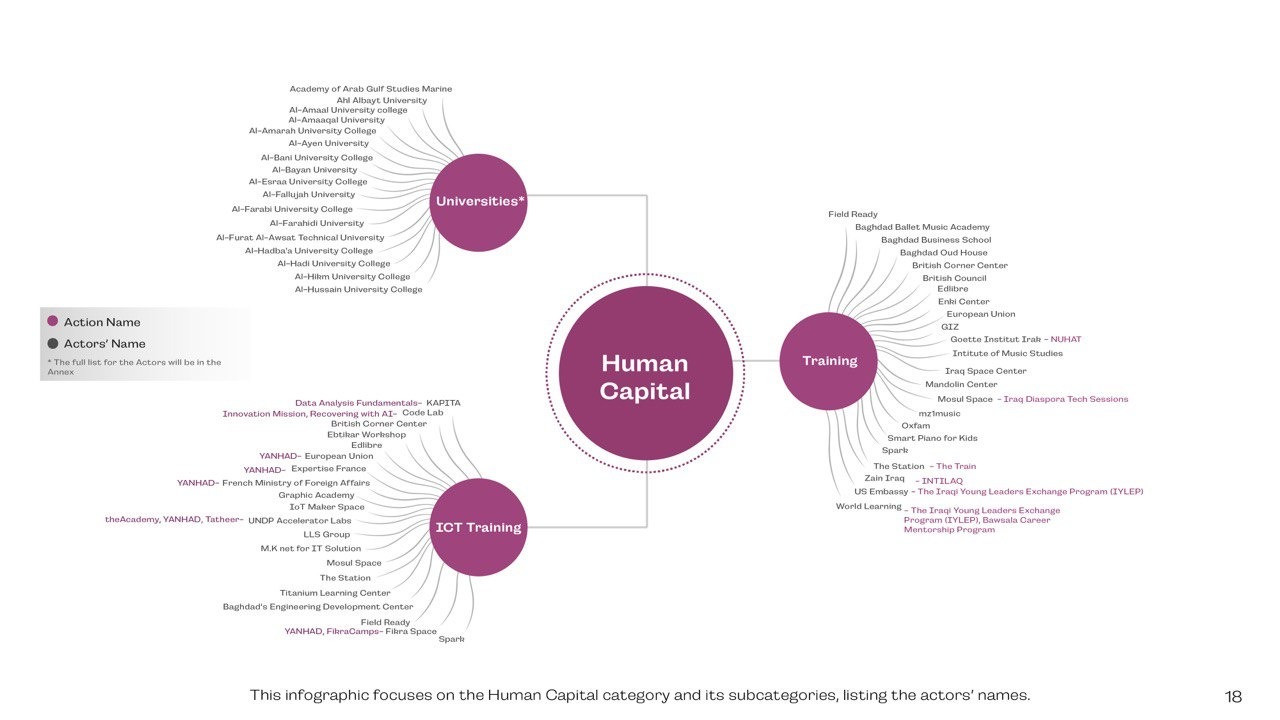
Human Capital
Research Limitations
The entrepreneurial ecosystem is a wide scope for one research to cover with the efforts of one institution. Hence, the research has its limitations. KAPITA has reached out to many actors in the scene to verify the information, however, we believe that the mapping would have been more inclusive with the participation of the rest of the actors in the ecosystem.
We hope, in the near future, that this entrepreneurial mapping will turn into an open-source project where everyone within the ecosystem can contribute to it. This will ensure that the project will be constantly up to date with all the new developments that are taking place in the Iraqi entrepreneurial scene.
Conclusion
The research is an attempt to map the Iraqi entrepreneurial ecosystem and present an inclusive picture of the main entrepreneurial activities. By conducting this research, we can observe that the Iraqi ecosystem has been witnessing continuous growth in the last few years. A trend of growth that we hope will continue for the next few years. While many ecosystem enablers and involved actors are working hard to fill numerous gaps, many areas are still in a nascent stage and require more projects and actors to be involved in. Plus, while it can be seen that many of the stakeholders are governmental entities, their involvements and contributions to the entrepreneurial ecosystem are not uniform and vary greatly.