Research Summary
KAPITA’s Research Department
The Reality of Information and Communication Technology In Iraq:
Ecosystem Reflection, Challenges, and Opportunities
ICT Overview
Information and communications technologies (ICT) is a generalized term that contains in its folds all devices, networking components, applications, and systems that allow people and organizations to interact with the digital world. Some of the most important components of ICTs are cloud computing, software, hardware, transactions, communication technology, data, and internet access. The importance of digital tools lies in what resilience they offer their users, such as easy and immediate access and rapid scalability. Iraq is still struggling with the digitization and digitalization of its government, and that includes government-to-business, government-to-government, and government-to-citizen services. Lack of proper infrastructure, laws, and human resources have made digitalization a more difficult deed.
Information and communications technology skills is an umbrella term that covers a wide range of technical skills. Therefore, in order to benefit from this research, a clear definition of such skills is required. Accordingly, we have categorized ICT skills into three different skill categories. Basic skills such as effective email correspondence, searching for information over the internet, using video conferencing applications (e.g: Zoom, Google Meets, Skype), using word processing software (e.g: Microsoft Word), using spreadsheets software (e.g: Microsoft Excel), and using presentation software (e.g: Microsoft PowerPoint).
Specialized skills such as digital marketing, social media management, graphic design (e.g: Adobe Suite), Business intelligence (BI) software (e.g: Tableau or Power BI), network and communications software (eg: Cisco, MikroTik), project management software (e.g: Trello, Jira, or Scrum), communication platform software (e.g: Slack or Discord), and other non-programming digital jobs (e.g: banking, finance, media).
Finally, programming digital skills including web development (e.g: front end, back end, UI/UX design, full-stack), desktop or enterprise development (e.g: Windows, MacOS, Linux applications), mobile application developers (e.g: iOS, Android, Windows), data science (e.g: data analysis, machine learning, business intelligence), database system engineering (e.g: SQL, NoSQL), and other programming domains (e.g: gaming).
This research aims to evaluate the digital skills levels of students, graduates, and employees, assess the private sector's digital skill demands, explore the individuals and ecosystem scene and challenges, and identify the available training opportunities.
As of January 2021, 75% of the Iraqi population have access to the internet, 61.4% of them are active social media users, and 98.4% have access to mobile connections. Furthermore, e-commerce is a growing field in Iraq, its growth however hindered by the limitations in the finance sector, with only 22.7% of the population aged 15 and above owning an account with a financial institution, 13.5% making purchases and/or paying bills online, and only 1.8% owning a credit card (DataReportal: Digital Iraq, 2021). The modern market is in high demand of ICT skills, with almost all businesses requiring some sort of ICT skill to assist in their growth. The 2019 COVID pandemic was a highlight for ICTs as it emphasized their importance, especially in contactless transactions of all sorts.
Labor Force Condition
The research examines the condition of the labor force through a series of assessments of the basic, specialized, and programming skills, in addition to analyzing the knowledge sources of those skills.
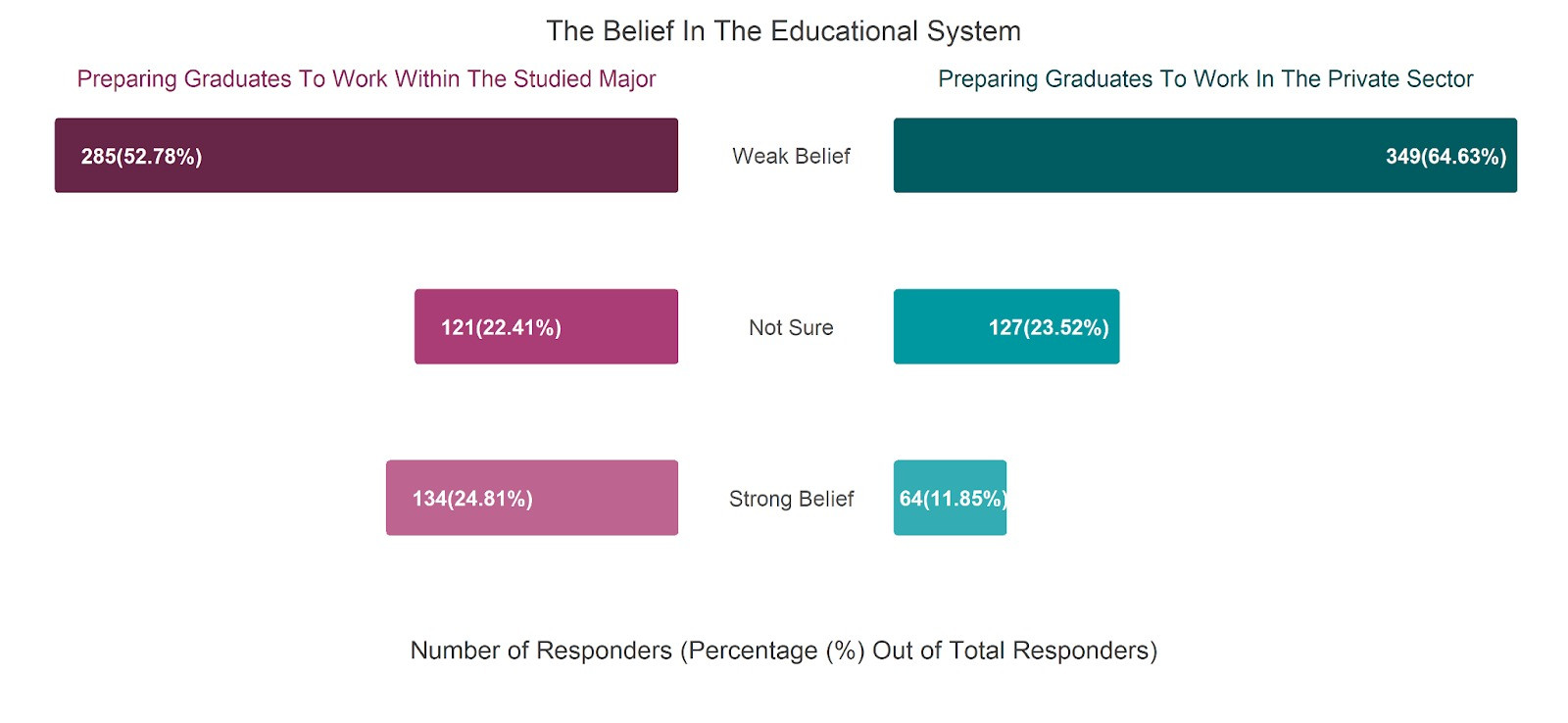
According to our survey of 540 respondents, the Iraqi education system seems very inadequate to accommodate the skills required to work in the private sector. It is contributing to a huge gap between the skills of the graduates of the system and the job market.
The majority of respondents believe that the educational system does not provide them with the proper set of skills to have a job in the private sector. However, it is interesting to note that around 25% of respondents thought that the education system is capable of preparing them to work strictly within their studied major.
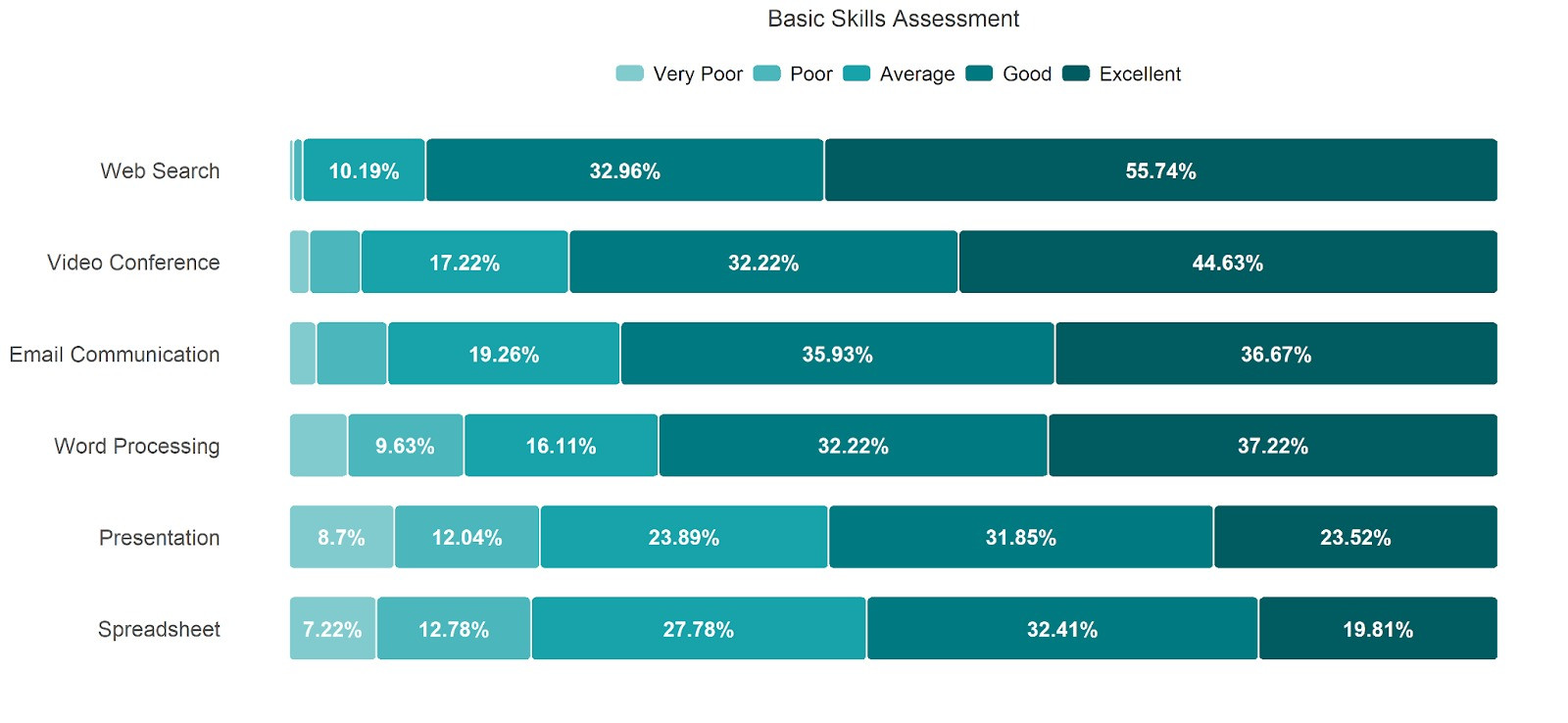
Almost 90% of all respondents were confident in being good at web search, followed by video conferencing while the majority fell short in terms of handling spreadsheets and preparing presentations. Most of these skills were self-taught, proving to be the most effective source of knowledge followed by trainings. Whereas respondents rated college education with a source of knowledge of average or poor benefit with around 32% and 28% respectively.
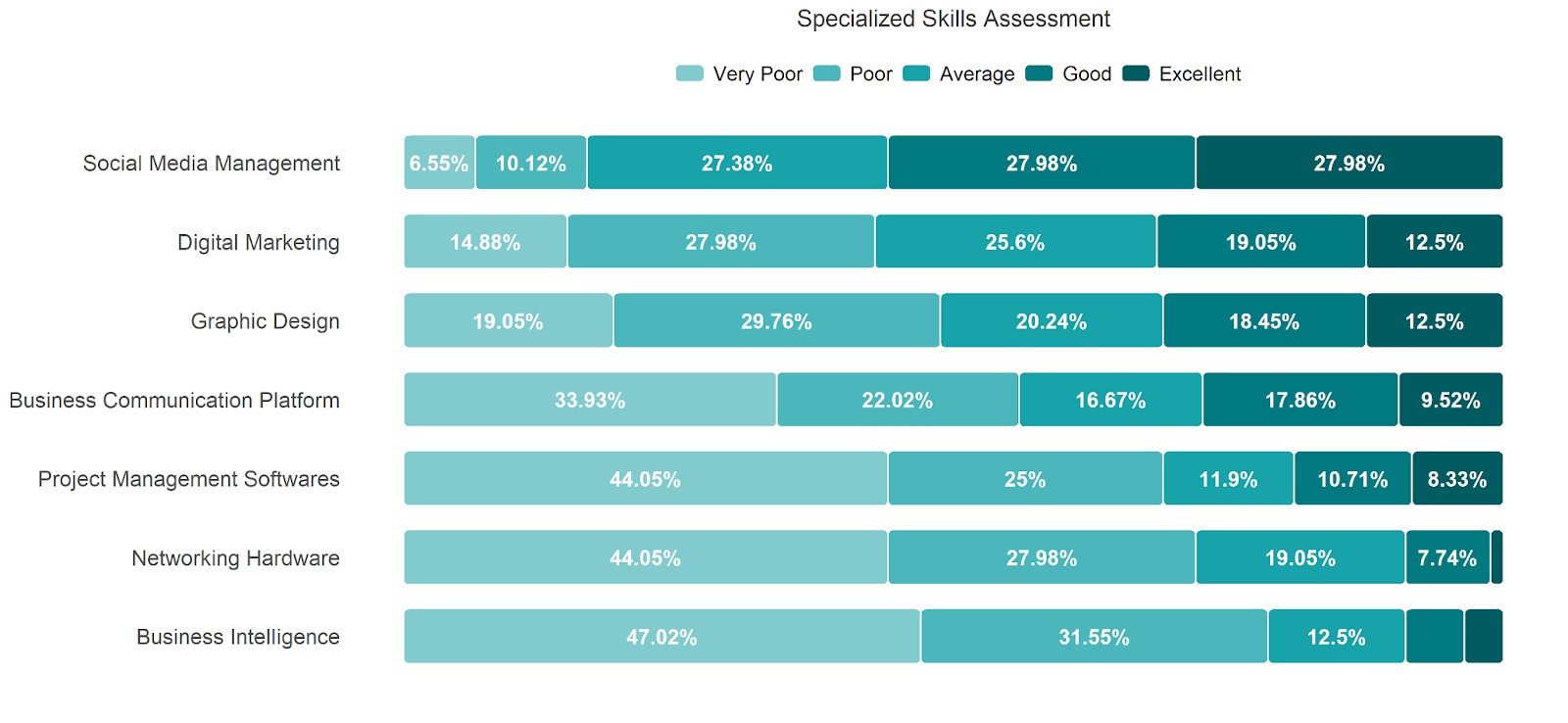
As for specialized skills, participants found themselves most knowledgeable in social media management and least knowledgeable in an aspect of business intelligence.
The source of knowledge of these skills showed a very similar pattern to that of basic skills, with self-taught being the one of excellent benefit for around 50% of the respondents followed by trainings. Once again, college education shows inadequacy as around 27% of respondents rated it as of poor benefit and 22% thought it was of very poor benefit.
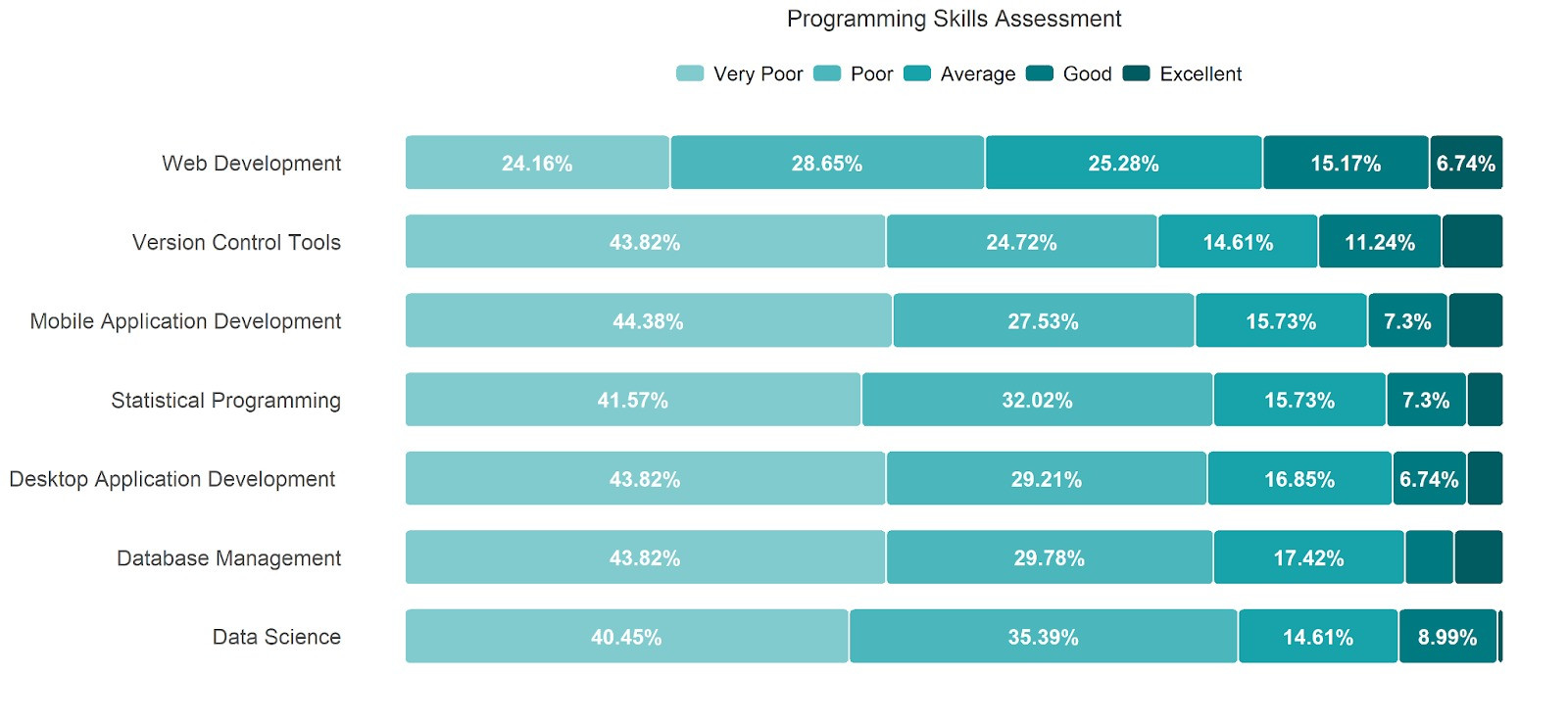
Programming skills were very clearly less available amongst the workforce compared to basic and specialized skills. Around 40%-44% of the respondents assessed their skills as very poor in all the examined programming skills except for web development that was assessed as poor and very poor by approximately 28% and 24% of the respondents respectively. The percentages of respondents who rated themselves as excellent in the aforementioned skills fell dramatically, with the highest percentage being an extreme low of 6.7% which was scored in web development, where the excellence assessment fell even behind that of other skills.
As for the source of programming skills, self-studying was still the source that yielded excellent benefit, however, to a lesser extent than non-programming skills as only 37% of respondents rated it as a source of excellent benefit compared to around 50% in basic and specialized skills. College education scored as a source of poor and very poor source of knowledge with around half of the respondents.
Private Sector Analysis
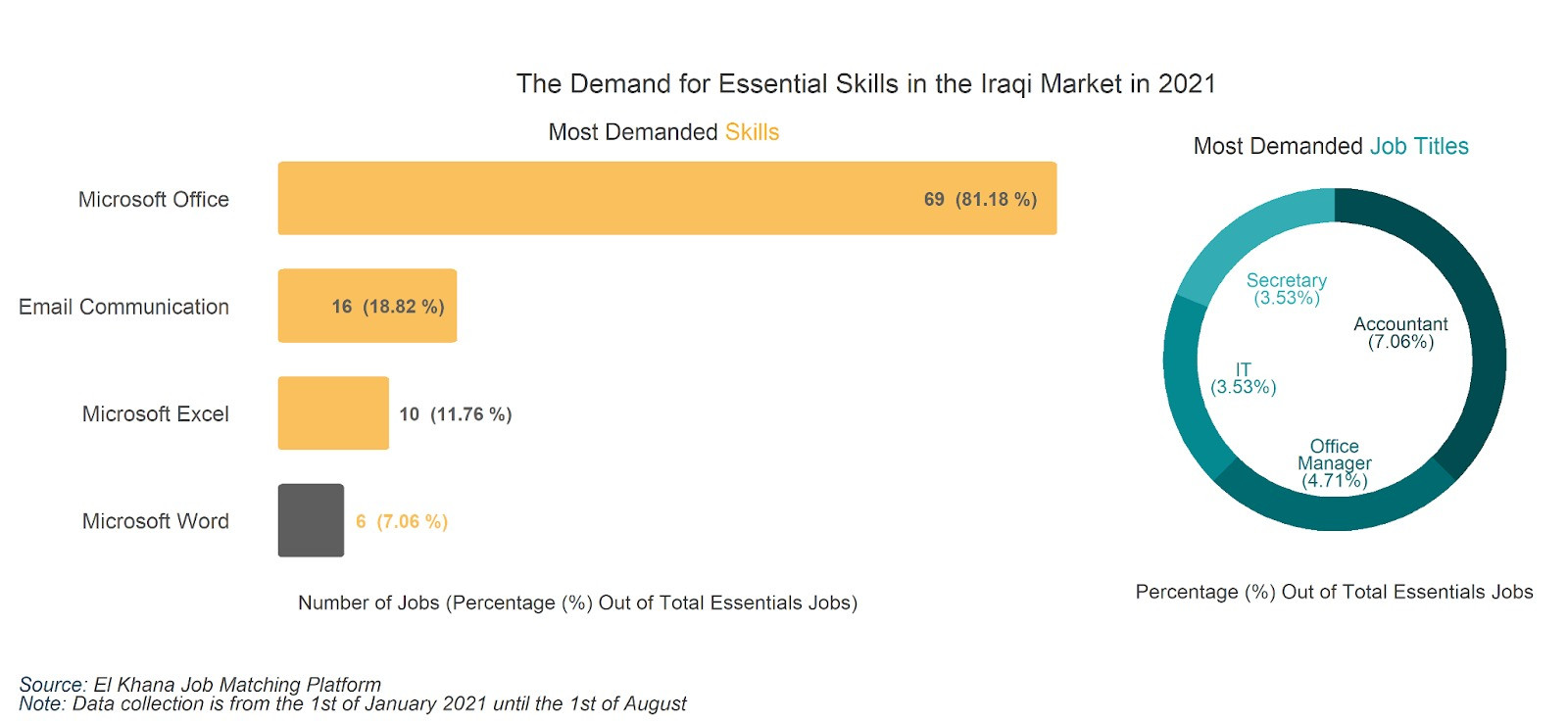
We reviewed 374 job postings and 1333 skills in the first half of 2021 to convey a holistic picture of the skills requirements of the Iraqi private sector. The overwhelming majority of 81% of postings required Microsoft Office skills and proper knowledge in the use of emails. Around 12% and 7% specified knowledge in using MS Excel and MS word, respectively. Out of all digital-related job postings during that period, 7% of them were looking for accountants, 4.7% for office managers, and 3.5% for a secretary and an IT officer.
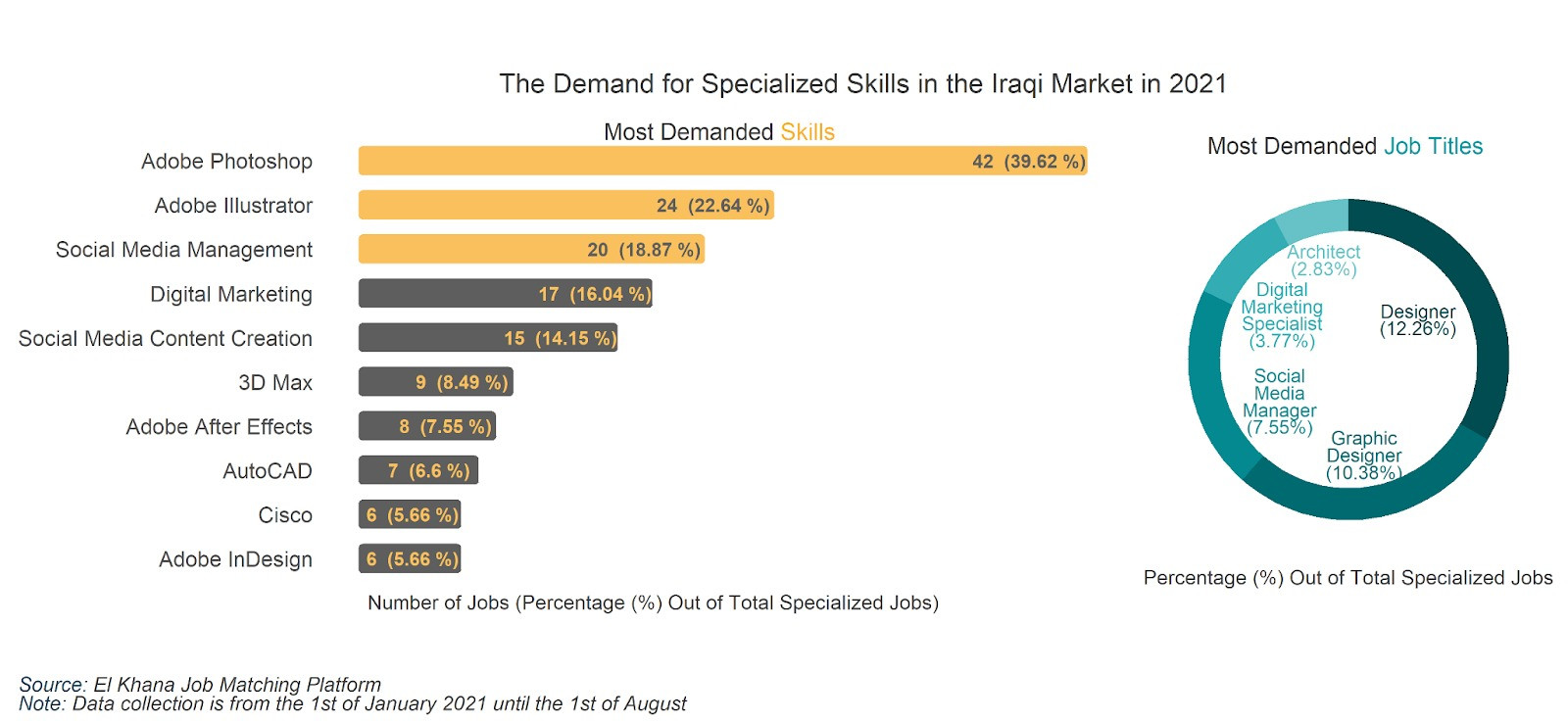
Moreover, Adobe Photoshop, Adobe Illustrator and social media management skills were the most frequently asked for skills in job applications for specialized skills across online job application platforms. The demand for designers was very high, occupying more than 12% of all digital job postings in the first half of 2021, and 10% of job postings asked for a graphic designer. Other job postings requested social media managers, digital marketing specialists, and architects.
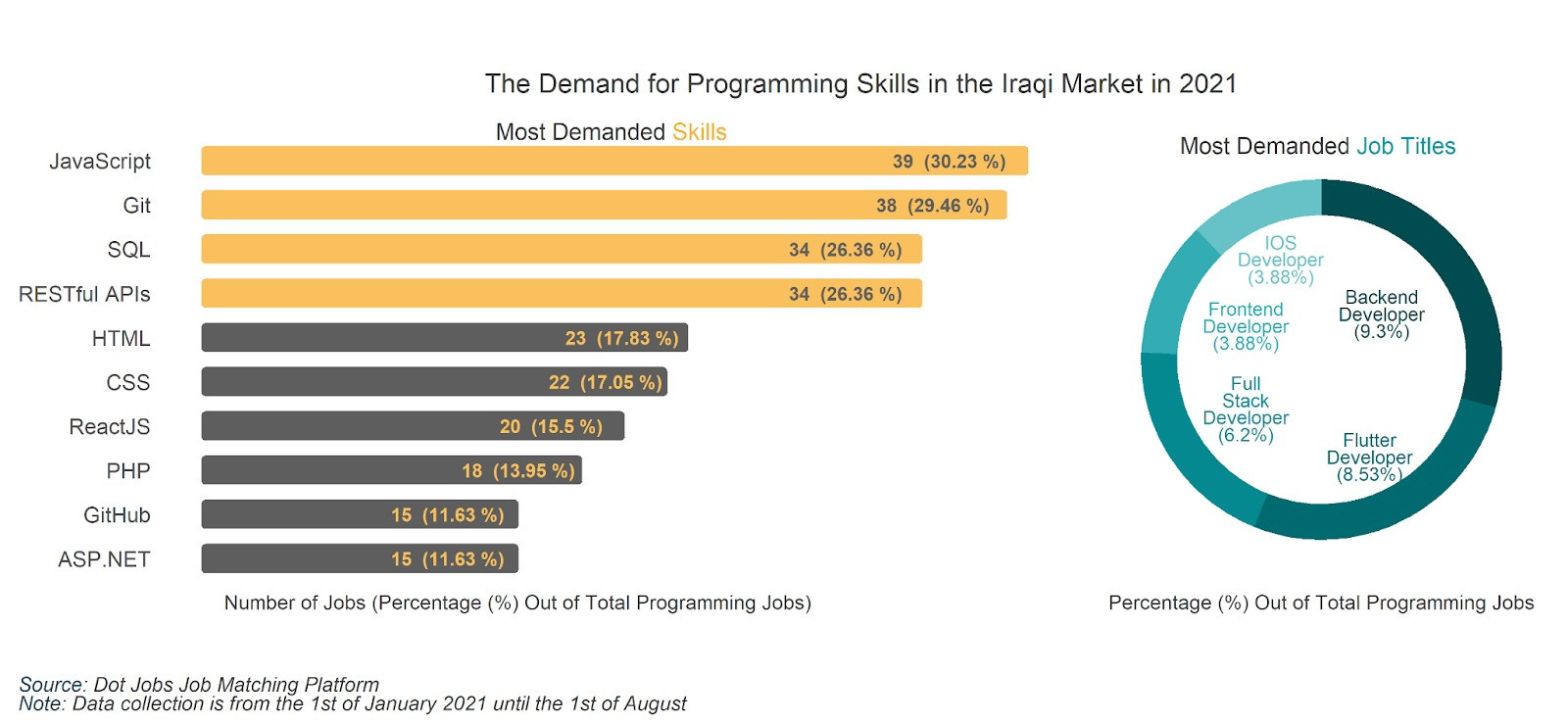
As for the programming digital skills, Javascript, Git, SQL, and RESTful APIs were the programming languages and skills most demanded in job applications across job platforms in the first half of the year 2021, with Javascript being the most demanded in more than 30% of all job offerings. Backend developers and flutter developers were the most requested job titles among the digital-related postings, taking up more than 9% and 8.5% of all digital job offerings, respectively. Other less-demanded positions were full-stack developer, iOS developer, and frontend developer.
Experts Opinions
The research extends into in-depth interviews with experts to provide valuable insights that will lay out the reasons behind the findings in the first parts of the research and will allow us to further understand the ecosystem from a different perspective.
The interviews were followed by critical thematic analysis and five major themes were identified. These themes draw a realistic scenario of the current ecosystem situation in a logical order, and they are as follows:
What Companies are Looking for:
Soft Skills: This set include core essential skills that most companies and hiring managers are seeking to find in their applicants regardless of the job position and level, this set includes problem solving, critical thinking, the ability and willingness to learn and develop one’s skills, effective communication, teamwork, taking initiative, leadership, commitment, hard work, adaptability, attitude, and ownership.
Hard Skills: The set of hard skills includes more technical skills and abilities that are easier to define, measure, and learn. Hard skills can comprise essential skills, specialized skills, graphic design skills, and programming skills.
The Current Recruitment Process:
The Mismatch Between the Job and Labor Markets: The current existing talents and level of skills in the market do not meet the job market demand, resulting in an unemployed workforce and plenty of job positions with no one to fill, especially senior positions. While regular job postings proved to be an ineffective method as a large number of applications are received but mostly submitted randomly and rarely match the job description or the minimum requirements.
Investment in Potentials: This approach is employed by some companies and startups, particularly those seeking young talents, to overcome the lack of skills in the market. They should invest in hardworking applicants with potential, willingness, and eagerness to learn and learn fast, then help those new employees develop by coaching and training them on the job.
Referrals: This has become a more reliable method to cut time, cost, and efforts for the company, where hiring managers use their networks, connections, and other employees in the company to share job position opportunities with their networks to find a suitable candidate. It is noteworthy that referrals do not entail providing unfair opportunities to certain applicants but rather match deserving individuals with jobs more efficiently. The applicants who got referred for the job still go through the recruitment process, the referral does not necessarily secure the job.
Outsourcing: The lack of existing senior-level skills and skills in certain domains like programming and graphic design, have led the hiring managers to resort to outsourcing foreign workforce for certain positions.
Key Identified Problems:
Ecosystem Issues:
Inadequate Academic Institutions: The interviewees unanimously agreed that our educational system needs drastic reformation as it does not equip Iraqis with the basic skills to prepare them for the job market and the curriculum is outdated.
Lack of Conceptualized Knowledge: This is found to be another critical issue in the ecosystem with many individuals knowing how to use the tools and technologies but falling short in understanding the bigger picture of the problems they are solving and cannot communicate the results effectively.
Lack of Advanced Technical Skills: Almost all the leading companies are facing a shortage of experienced technical people, especially when it comes to specific niche areas with high demands and domains such as graphic design. This deficiency forces companies to hunt for the very few talented skills in the market.
Brain Immigration: Many highly skilled and well-trained professionals left Iraq due to the poor ecosystem and lack of support. This immigration continues to cause a shortage of senior-level talents within the community.
Labor Issues:
Insufficient Self-investment: This is a serious drawback that became a norm within the Iraqi community. This problem is clustered around the lack of a self-learning mentality, ineffective time management, and absence of leadership. Adding to this, a senior director explained that the youth need to understand prioritizing self-investment rather than chasing money, especially at the beginning stages of their careers.
Soft Skills Gap: This is among the top concerns for private sector companies. ِAccording to a chief administrative officer, many Iraqi people are not trained for work environment situations, this entails proper behavior towards their peers and managers, and preparations for interviews which involves resume writing, a healthy attitude during work, and ownership.
Dependent-mindset Issues: have surfaced as a significant concern. A major contributor to the private sector explained that the mindset of relying on governmental jobs after graduation and not thinking about taking initiatives is found in a big portion of the community. He added that Iraqis should learn how to be independent and creative workers as opposed to the current situation where employees have to be micromanaged by their supervisors.
English Language Barrier: This is a main challenge in the private sector as it is a must-have skill for individuals. However, the current ecosystem lacks even the basic English language usage such as professional communication through emails.
Reluctance to Change: Many Iraqis are sitting each in their comfort zone without any attempt to advance their skills. One manager added, “Some Iraqis just want to get to the end of the month to receive their paycheck”.
Seeking Shortcuts to Success: Some individuals do not progress through the learning path gradually, thinking that they can learn everything in a very short time. This fact is coupled with the unwillingness to read books, articles, or even take online courses to develop their skills is causing a skill gap in the market.
Creating Talent Magnet Companies.
Company Culture and Work Environment: Building the right company culture and creating a healthy and friendly working environment are extremely vital to creating a talent magnet company and building a strong pipeline for the ecosystem. If a company succeeds in creating the right culture, then it will have gained leverage when trying to acquire and retain employees and talents.
Career Development: A crucial step for creating a talent magnet company involves the ongoing development of the company and its employees to keep up to date with the rapid pace at which things are changing in the world and to promote the growth of the company. Moreover, the company should prioritize every individual employee’s career and establish a clear path for them to encourage their development.
Gender-Specific Limitations.
Social and Cultural Barriers: Women in Iraqi society still struggle with many barriers that limit their opportunities. Outdated traditional mindset still discourages women to work or limits them to stereotypical job roles and duties, preventing them from exploring their passions, dreams, and potentials. Although society has come a long way in recent years, there is still a long way to go, the progress that has been made in cities like the capital is not tangible everywhere.
The lack of Women Involvement in the Tech Sector: There is a wide gap between the number of women and men working in the tech domain. One expert reported only 11% of the programming team in their organization were women, even though they aim to achieve an equal quota for men and women, they stated “we still receive a scarce number of women applicants for those positions, often with fewer skills than men”. Another expert stated that “There is an obvious skill gap between women and men working in the tech domain since this area is already male-dominated and requires a lot of self-learning and engagement with others, it is harder for women to break into it, which affects the quality of their skills”.
Job Preference: Some experts noticed that there are certain jobs that women favor over others and tend to be more willing to pursue. One expert reported that “we are more likely to find women working in jobs related to social media, given that they exercise better patience, flexibility, and engagement.” Whereas jobs related to sales are mostly unfavorable to women, even though organizations try to be sensitive regarding the clients they deal with and the locations they dispatch their female employees to.
Applications Approach: Experts have observed that women applicants tend to be more apprehensive and less assertive in their applications. They are also more likely to apply to job positions when they match the majority of skills, qualifications, and experience listed in the job application. Unlike men who are more open to applying for positions even when they do not possess all the required qualifications.
Download the full report overview
Download the 5th Business LANDSCAPE Magazine
